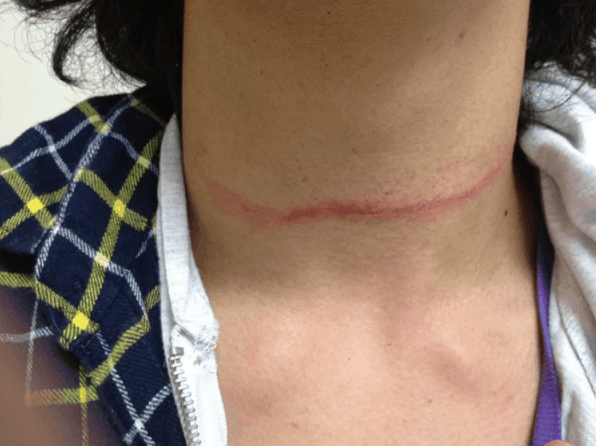
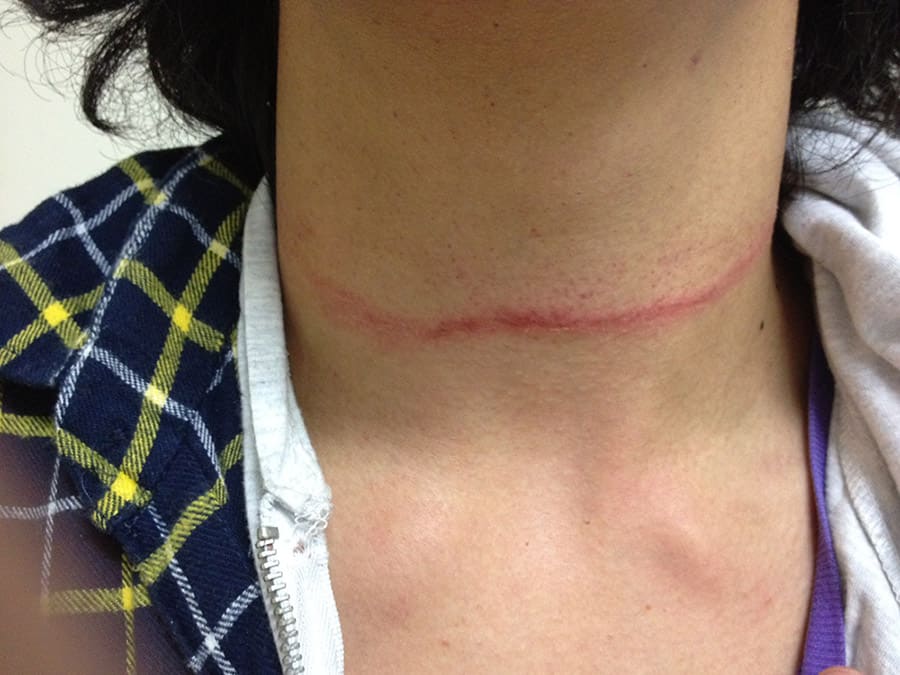
 I was considering writing a blog on the patient who presents post hanging, when I had a patient with this presentation come in today. The classical understanding of hanging as it was used as a form of capital punishment, was really a form of decapitation. The result of was a fracture of the upper cervical spine, usually C2 and a transection of the cord. It was not unusual for the the head to separate from the torso.
I was considering writing a blog on the patient who presents post hanging, when I had a patient with this presentation come in today. The classical understanding of hanging as it was used as a form of capital punishment, was really a form of decapitation. The result of was a fracture of the upper cervical spine, usually C2 and a transection of the cord. It was not unusual for the the head to separate from the torso.
The adult patient with hanging we see in the Emergency Department today, is always a result of suicide attempt. In most cases it is a form of strangulation.
What are we concerned about, when the call comes in, that a patient is being brought in post hanging?
2 Types of Hangings
- Suspension: rope tied around the neck and the person suspended so that the ligatures tighten. These are the most common forms of hanging presentation into the emergency department.
- Drop: The body is dropped from a distance with the aim of causing cervical spine fracture and spinal cord injury. This is an example of judicial hanging.
There are really 3 areas of concern:
1 Cervical Spine Injury – Although this causes significant concern, it occurs in less than 1% of cases and is associated with a fall of greater than body height(Hangman Fracture).
2 Airway – The airway can deteriorate very rapidly. However the airway should not pose a problem, unless there is a cricoid or thyroid fracture. In the strangulation patient, the airway is not usually the cause of death, as there have been instances of deaths from hangings, in patients with tracheostomies.
3 Vascular Injuries –
(a) Venous Obstruction can lead to cerebral hypoxia
(b) Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow may occur secondary to arterial spasm
(c) Bradycardic Collapse can occur secondary to carotid sinus pressure.
4 Other Injuries
Thyroid or Cricoid cartilage fractures
What Investigations do I do?
Image the cervical spine if concerned, however the chance of a fracture is low.
Cat Scan- Scan the neck if there is any chance of a thyroid or cricoid fracture. A hoarse voice, or change in voice may be a clue. Scan the head if there is agitation as it may indicate cerebral oedema.
Disposition
Every case is different. The patient will require psychiatric evaluation. Be careful of those patients that have had a significant episode, but look well. It may be appropriate to admit overnight and watch primarily for airway swelling.