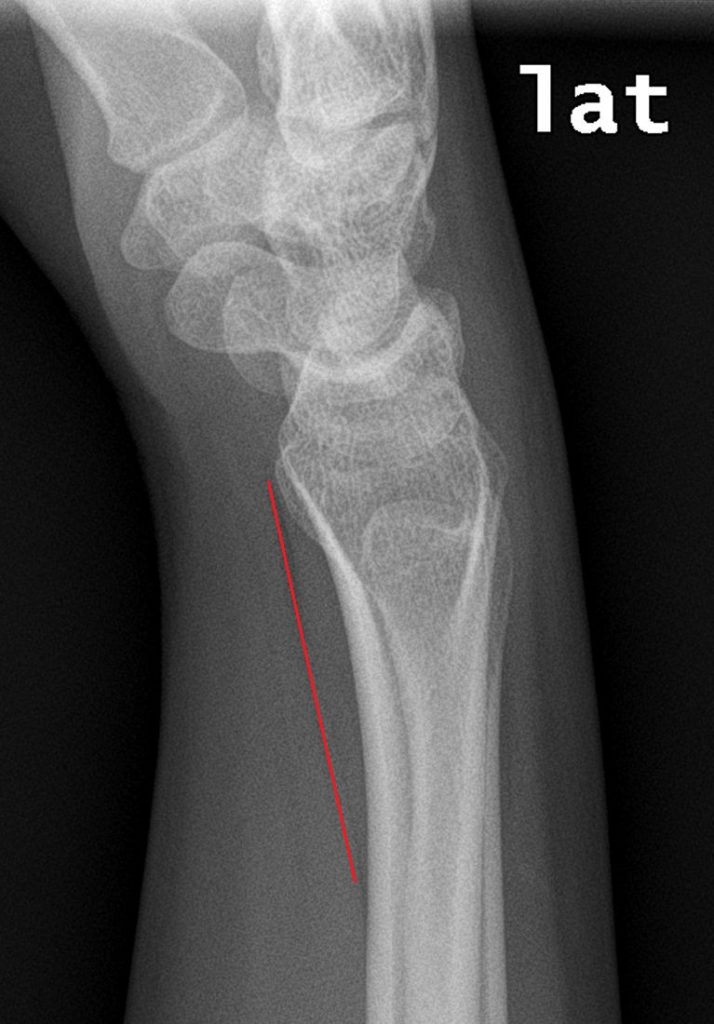
The pronator Quadratus sign is a sign seen on the lateral X-ray of the wrist/forearm and can assist in diagnosing an occult radial fracture.
The line represents a fat pad that lies parallel to the distal radius, over the fascial covering between pronator quadratus and flexor digitorum profundus muscle. The line runs from the palmar radial tip parallel to the radial shaft. If it is displaced or bowed, it can indicate that there is a distal radial fracture, even if one is not evident.
It has been suggested that a displacement of >8mm in females and >9mm in males is abnormal.
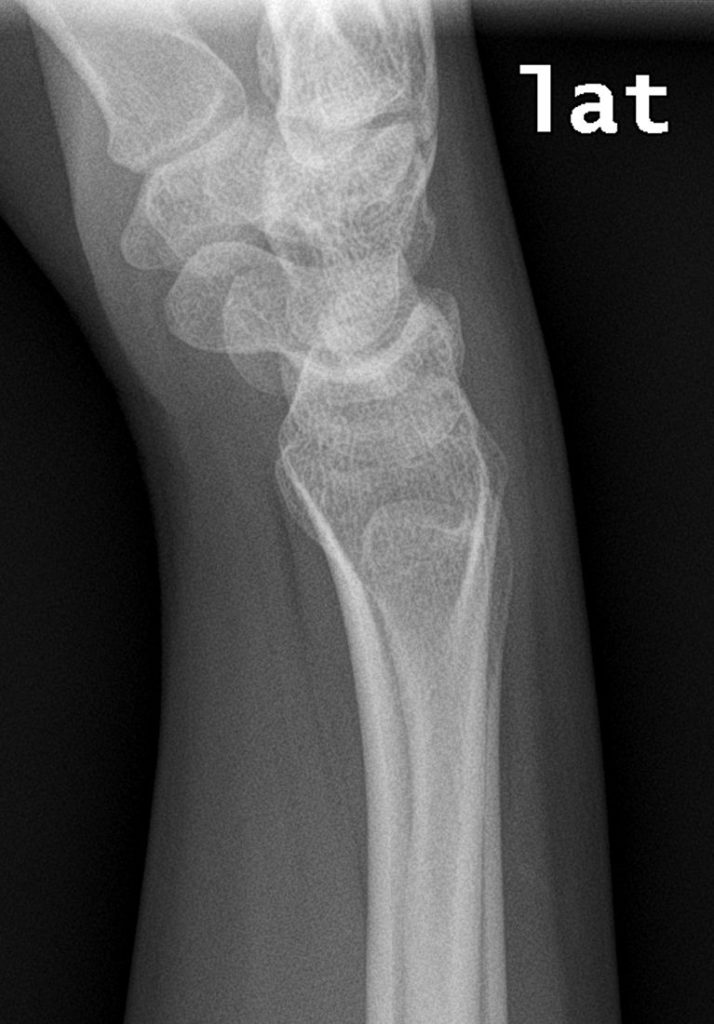
Below is a normal Pronator Quadratus Fat pad sign
+ve pronator quadratus sign: a case
A patient presents following a fall onto outstretched hand. X-rays are done due to the patient having significant distal radial pain.
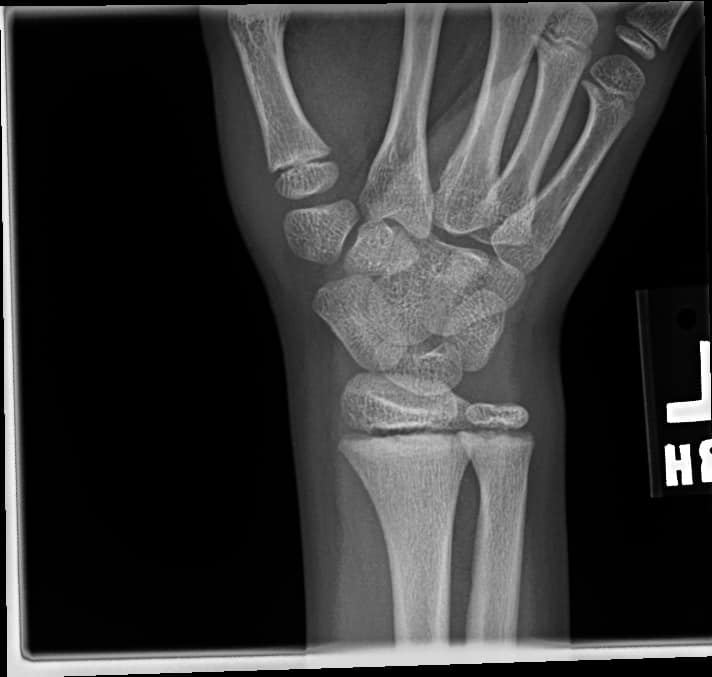
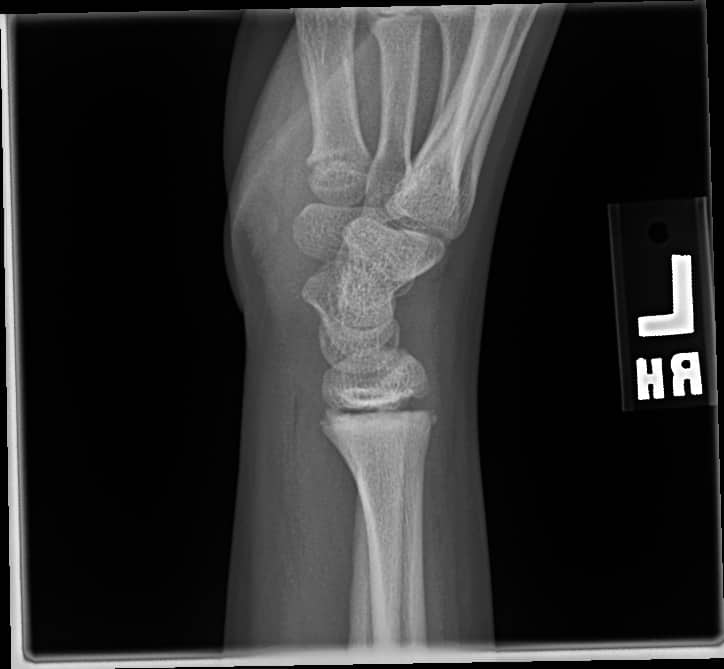
In the above X-ray we see that the fat pad sign is pushed away from the radius, certainly > 9mm. This is positive for a fracture. It is annotated below.
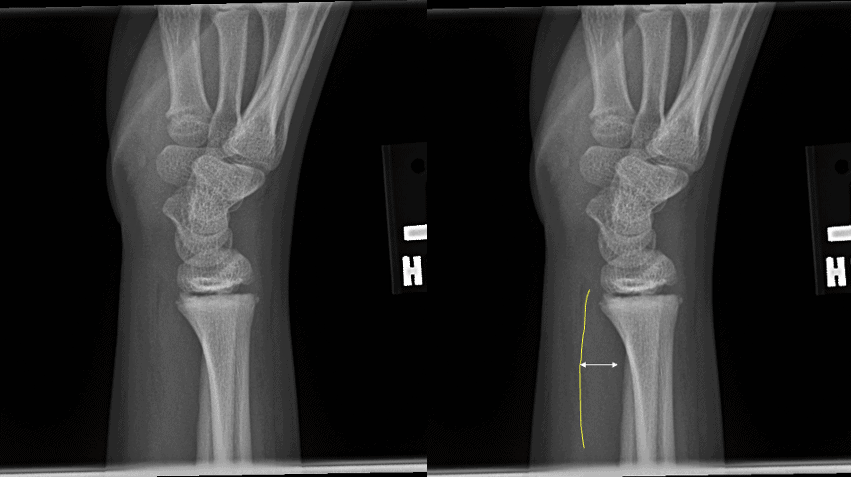
Use the Pronator Quadratus Sign next time the xray looks normal but you clinical examination gives you a high pre-test probability. The sign is specific, but not as sensitive, so a negative sign does not exclude a fracture.



